
|
Flow4J-Struts IntegrationThe following sections describe the advantages of using Flows as the Controller part of the Struts framework and a detailed description how to integrate Flow4J in Struts.
You can see live samples at
Flow4J-Struts Samples
Note:
MotivationThe Flow4J framework contains a Servlet that dispatches a user request directly to a specific flow. All the request parameters are put in the Flow Dictionary as String. This is all fine, but the user has to code the validation stuff and has to care that in the case of validation errors the old values are again displayed for further correction. Thus Flow4J represents the controller in the MVC pattern itself but cannot compete with some others like the Apache Struts framework which offers nice and useful features like validation and a rich tag library to access information in Form Beans. I personally don't like Struts very much because it becomes more and more a mammoth and tries to cover too much aspects of web application programming. What IMO is very complicated in Struts is all this XML configuration and the fact that each Action has to return a forward mapping that is directly tied to a resource like a JSP page, and unfortunately this mapping again has to be declared in XML form. Cha ining many Struts actions together is also only possible by XML. IdeaAt this point comes the idea to use Struts features like Form Beans, their validation and even tiles, but replace single Actions by complete Flows. So the whole business process is not only one Action class that is a non-visualizable sequence of method calls, but a complete Flow that can execute a number of tasks and can even contain flow controlling functionality like decisions, jumps, and joins. The fact that Flows have one or more well defined entry points (Start Flowlets) and can return a template or resource name, makes it possible to transfer many Struts configuration information out of the struts-config.xml file directly into the flow, where they belong. Almost all URLs which trigger the Struts controller have the following pattern: http://server/context/someaction.do This requires a mapping in the struts-config.xml file. The Flow4J-Struts integration simplifies this: http://server/context/SomeFlow-Start.do This URL pattern is much more self explaining and requires no manual configuration because the framework automatically recognizes which Flow to execute. Let's see the details and the possibilities to involve Form Beans and validation in the next section. RealisationThe main building parts of the Struts framework are
developers normally declare them in the struts-config.xml file.
In the Flow4J Designer, Start Flowlets have a dynamically extendable property list.
This means that you specify a c
omma separated list of property names, and Eclipse
generates the Property Descriptors automatically. In the the next picture you can see
the properties of the Start Flowlet "Check".
These properties are needed to teach Struts what to do if the user calls the following URL: http://server/context/Login-Check.do?user=...&password=... 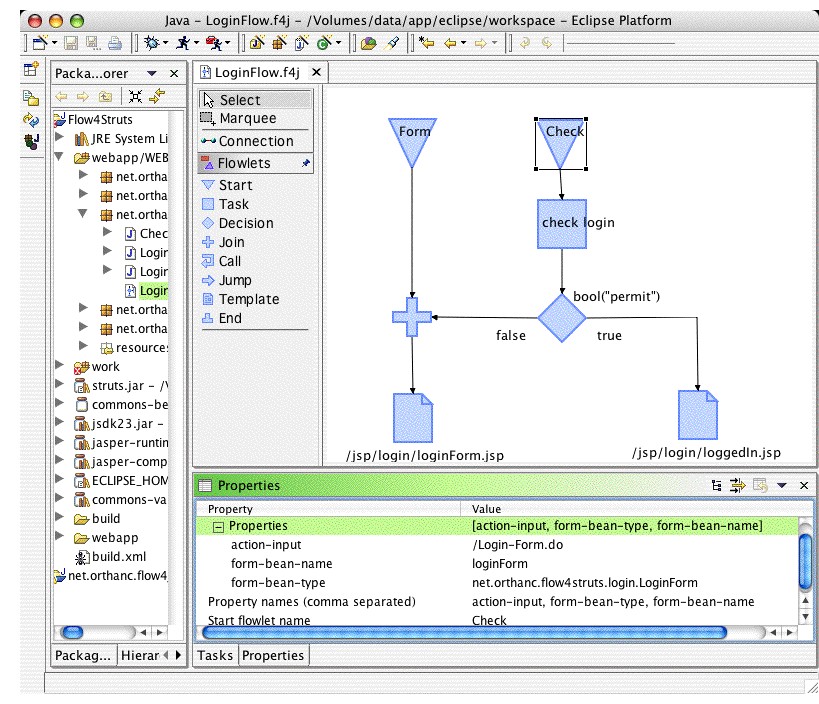
The advantage of this way of Struts configuration is that all information that belongs together is kept together . That's why the declaration of the Form Bean's name and type is done directly in the Start Flowlet. BTW a Flow can have more than one entry point (Start Flowlet) thus the possibility is also given to declare different Form beans for the different Start Flowlets of the same Flow. Flow4J is very tolerant and gives priority to all information that Struts gets out of the struts-config.xml file. This means that you can distribute Form Bean and Action informations between the Flow and the struts-config.xml file. Thus there exist the following two possibilities to declare a Form Bean:
If the type is declared in both locations, and they are not the same, then an exception is thrown. Technical Acpects
Flow4J uses the Struts API to register all Actions and ActionForms.
For this reason all Flows which are registered at the
In this case Flow4J is tolerant again, you can declare additional information in the struts-config.xml file
eg. for the Action Mapping with the path "/Login-Form". But if nothing else is specified the config file,
the Action's type is by default
configuration
The configuration of the web applicaion is quite the same as with the other Flow4J Servlets.
The Servlet type is the extended
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?>
<!DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC "-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.3//EN"
"http://java.sun.com/dtd/web-app_2_3.dtd">
<web-app>
<display-name>Flow4j-Struts demonstration</display-name>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>action</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>net.orthanc.flow4j.runtime.connectors.struts.Flow4JActionServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>config</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/config/struts-config.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>flow-repository-class</param-name>
<param-value>net.orthanc.flow4struts.FlowRepository</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>action</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.do</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
...
</web-app>
All needed classes are in the file
|